The Role of HBA1C Levels
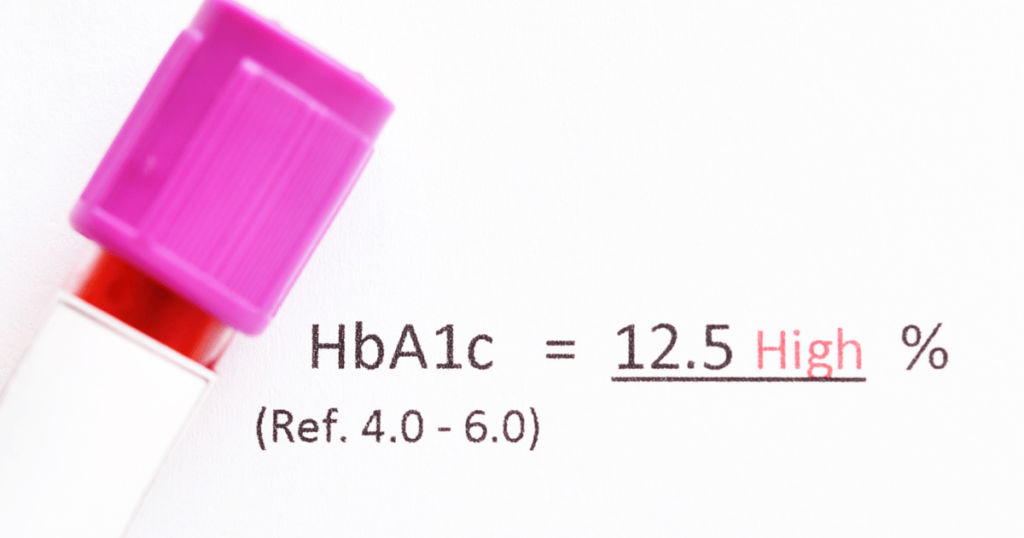
Diabetes management is a critical aspect of maintaining a healthy lifestyle for those diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes. HBA1C Level is One of the most significant markers for monitoring diabetes, a term that often surfaces in doctor’s offices and diabetes management discussions. This article delves into the role of HBA1C levels in managing Type 2 diabetes, offering insights into how understanding and controlling these levels can lead to better health outcomes.
Understanding HBA1C Levels
Before diving into the management strategies, it’s essential to understand what HBA1C levels signify. HBA1C, also known as glycated hemoglobin, is a form of hemoglobin that is chemically linked to glucose. The HBA1C test measures the average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months. This measurement is crucial because it provides a long-term view of blood sugar control, unlike daily glucose testing, which only offers a snapshot.
Why HBA1C is Important in Type 2 Diabetes
In Type 2 diabetes, the body either resists the effects of insulin – a hormone that regulates the movement of sugar into cells – or doesn’t produce enough insulin to maintain normal glucose levels. Regular monitoring of HBA1C levels helps in:
- Tracking Disease Progression: It shows how well you are managing your diabetes over time.
- Treatment Adjustment: Helps in adjusting medications or dietary choices.
- Risk Reduction: Lowering HBA1C levels reduces the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Ideal HBA1C Levels
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends an HBA1C goal of less than 7% for most adults with diabetes. However, this target can vary depending on individual health conditions, age, and risk of hypoglycemia. It’s crucial to consult with healthcare providers to determine a personalized HBA1C target.
Strategies for Managing HBA1C Levels
Managing HBA1C levels involves a combination of lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and possibly medication. Here are some effective strategies:
1. Diet and Nutrition
A balanced diet plays a pivotal role in managing Type 2 diabetes. Focus on:
- Low Glycemic Index Foods: These foods have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels.
- Fiber-Rich Diet: High-fiber foods, like whole grains, help in controlling blood sugar levels.
- Controlled Portion Sizes: This helps in maintaining a healthy weight, crucial for diabetes management.
2. Regular Physical Activity
Regular exercise can help increase insulin sensitivity, meaning your body can better use the available insulin to absorb glucose. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity per week.
3. Medication Adherence
If you are on diabetes medication, taking it as prescribed is crucial. Medications play a significant role in keeping your blood sugar levels in check.
4. Regular Monitoring
Apart from the HBA1C test, regular blood glucose monitoring at home is vital. It helps in making immediate adjustments to your diet or exercise routine.
5. Stress Management
Stress can affect blood sugar levels. Techniques like mindfulness, yoga, or even regular exercise can help manage stress.
The Impact of Lowering HBA1C
Lowering your HBA1C levels can have a significant impact on your overall health. It reduces the risk of diabetes-related complications such as:
- Heart Disease and Stroke
- Kidney Disease
- Vision Problems and Blindness
- Nerve Damage
When to Test for HBA1C
The frequency of HBA1C testing depends on your treatment plan and how well your diabetes is controlled. Typically, it’s recommended to test at least twice a year. However, if you’re undergoing treatment changes or not meeting your glycemic goals, more frequent testing may be necessary.
Challenges in Managing HBA1C
While managing HBA1C levels is crucial, it comes with its challenges. These include:
- Understanding Carbohydrate Counting: Learning to count carbs can be overwhelming but is essential for blood sugar control.
- Medication Side Effects: Some diabetes medications can have side effects, making adherence challenging.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Making long-term lifestyle changes requires consistent effort and motivation.
Conclusion
Managing Type 2 diabetes is a multifaceted approach, with HBA1C levels playing a central role. By understanding the importance of these levels and implementing strategies to control them, individuals with Type 2 diabetes can lead healthier lives. Remember, managing diabetes is not just about controlling blood sugar levels but also about making sustainable lifestyle changes. Regular consultations with healthcare providers, personalized treatment plans, and self-management education are key to successful diabetes management.
Note: This article is intended for informational purposes and does not substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with healthcare professionals for individualized medical and dietary advice.
Everything You Need To Know About Gestational Diabetes You don’t wanna miss this Simple Explanation



