Explore the nuances of diabetes through a detailed examination of type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Uncover the distinctive symptoms, delve into the intricacies of continuous glucose monitoring, and understand the impact of a tailored diabetic diet. This guide provides valuable insights for individuals seeking to comprehend the differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes and manage their condition effectively.
- Introduction
- Type 1 Diabetes: Understanding the Basics
- Type 2 Diabetes: Unraveling the Complexity
- Diabetes Symptoms: A Shared Perspective
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Technological Leap
- Diabetic Diet: Tailoring Nutrition for Diabetes
- Blood Sugar Monitor: A Vital Companion
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Decoding Diabetes: A Comprehensive Guide to Type 1 Diabetes vs Type 2 Diabetes
Diabetes, a pervasive health condition affecting millions globally, is not a one-size-fits-all diagnosis. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on the distinctions between type 1 and type 2 diabetes, exploring symptoms, monitoring techniques, and dietary considerations.
Type 1 Diabetes: Understanding the Basics
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This results in a deficiency of insulin, the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels. Key features of type 1 diabetes include:
- Onset: Typically diagnosed in childhood or adolescence.
- Insulin Dependency: Individuals with type 1 diabetes require insulin injections for survival.
- Symptoms: Common symptoms include excessive thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, and fatigue.
Type 2 Diabetes: Unraveling the Complexity
- Insulin Resistance: Unlike type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes often involves insulin resistance, where the body’s cells do not respond effectively to insulin.
- Lifestyle Factors: Sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, and genetic predisposition can contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes.
- Onset: Commonly diagnosed in adulthood, but increasingly prevalent in younger individuals due to lifestyle changes.
- Management: Treatment may involve lifestyle modifications, oral medications, and, in some cases, insulin therapy.
Diabetes Symptoms: A Shared Perspective
While type 1 and type 2 diabetes have distinct origins, they share common symptoms that serve as early indicators for both conditions:
- Increased Thirst
- Frequent Urination
- Unexplained Weight Loss
- Fatigue
Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for prompt diagnosis and effective management, irrespective of the diabetes type.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Technological Leap
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) has transformed diabetes management by providing real-time insights into blood sugar levels. Key aspects of CGM include:
- Real-time Data: CGM devices offer continuous updates on blood sugar levels, allowing for timely interventions.
- Precision in Management: CGM enables individuals to make informed decisions about insulin dosage, diet, and lifestyle choices.
- Improved Quality of Life: By reducing the frequency of fingerstick testing, CGM enhances the overall experience of diabetes management.
Diabetic Diet: Tailoring Nutrition for Diabetes
- Balanced Nutrition: A diabetic-friendly diet focuses on whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables, promoting stable blood sugar levels.
- Carbohydrate Management: Understanding and monitoring carbohydrate intake is crucial for effective blood sugar control.
- Meal Timing: Consistent meal timing helps regulate blood sugar levels, preventing sudden spikes or drops.
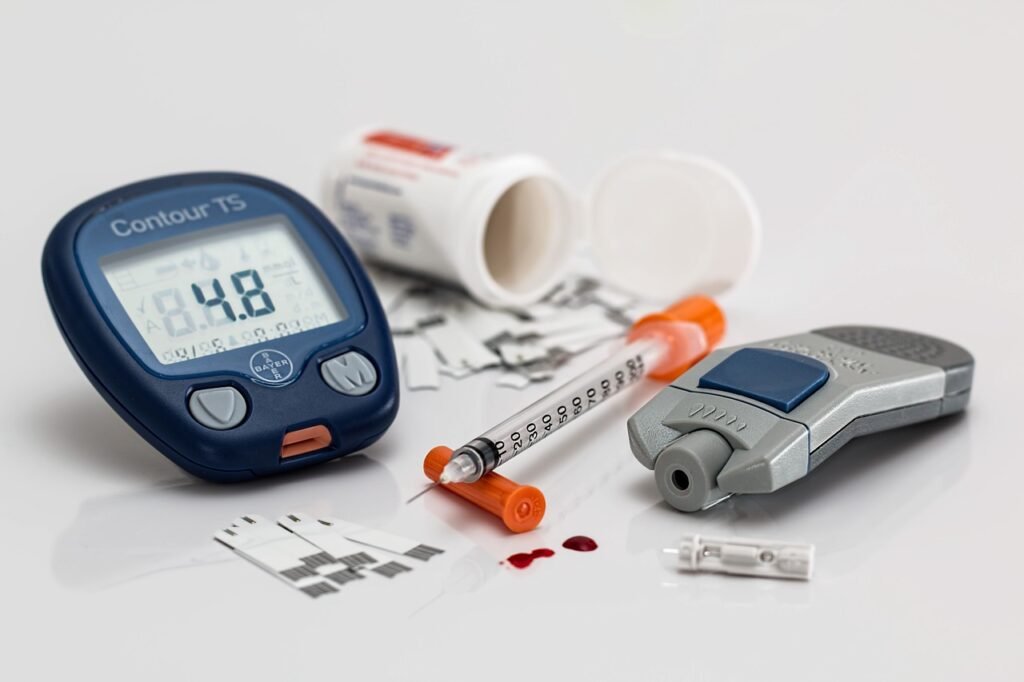
Blood Sugar Monitor: A Vital Companion
Regular blood sugar monitoring is essential for individuals with diabetes. Key considerations for choosing a blood sugar monitor include:
- Accuracy: Ensuring the monitor provides precise and reliable readings.
- Ease of Use: User-friendly features enhance the monitoring experience.
- Portability: Compact, portable monitors facilitate on-the-go testing, empowering individuals to manage their condition actively.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Can type 1 diabetes develop later in life? A1: While type 1 diabetes is commonly diagnosed in childhood, it can develop at any age.
Q2: Is insulin therapy only for type 1 diabetes? A2: No, insulin therapy may be prescribed for some individuals with type 2 diabetes to effectively regulate blood sugar levels.
Q3: How often should blood sugar be monitored? A3: The frequency of blood sugar monitoring varies but is typically recommended multiple times a day, especially after meals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes is crucial for effective management. By recognizing symptoms, embracing continuous glucose monitoring, adopting a diabetic-friendly diet, and regularly monitoring blood sugar levels, individuals can proactively navigate the complexities of diabetes. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource for those seeking to enhance their knowledge and take charge of their diabetes journey.



