Explore the nuanced world of diabetes as we delve into its types, Symptoms And Treatement options. Uncover the significance of continuous glucose monitoring, decipher the differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes, and discover the impact of a tailored diabetic diet. Empower yourself with knowledge about blood sugar monitoring for a proactive approach to diabetes management.
- Introduction
- Understanding Diabetes Symptoms
- Distinguishing Between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
- The Role of Continuous Glucose Monitoring
- Navigating Diabetic Diets
- Significance of Blood Sugar Monitoring
- Effective Treatments for Diabetes
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Symptoms And Treatement
Diabetes, a prevalent chronic condition, affects millions worldwide. In this comprehensive guide, we unravel the intricacies of diabetes, exploring symptoms, types, and innovative treatments. From distinguishing between type 1 and type 2 diabetes to understanding the impact of continuous glucose monitoring, we delve into the critical aspects of diabetes management.
Understanding Diabetes Symptoms
Recognizing diabetes symptoms is paramount for early intervention. Common signs include increased thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, and fatigue. It’s crucial to note that symptoms may vary between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. By staying vigilant to these signals, individuals can seek prompt medical attention, facilitating timely diagnosis and management.
Distinguishing Between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
- Type 1 Diabetes: Type 1 diabetes, often diagnosed in childhood, results from the immune system attacking insulin-producing cells. This type necessitates insulin injections for survival.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Predominantly associated with lifestyle factors, type 2 diabetes develops when the body becomes insulin resistant. Lifestyle modifications, oral medications, and, in some cases, insulin therapy are essential components of type 2 diabetes management.
The Role of Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) revolutionizes diabetes management by providing real-time insights into blood sugar levels. This technology empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and insulin intake. CGM not only enhances precision but also offers a proactive approach to diabetes care.
Navigating Diabetic Diets
- Balanced Nutrition: Crafting a diabetic-friendly diet involves prioritizing whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables. These choices contribute to stable blood sugar levels and overall well-being.
- Carbohydrate Counting: For effective blood sugar control, understanding and monitoring carbohydrate intake are vital components of diabetic dietary management.
- Meal Timing: Consistent meal timing can aid in blood sugar regulation. Spreading meals throughout the day helps prevent sudden spikes or drops in blood glucose levels.
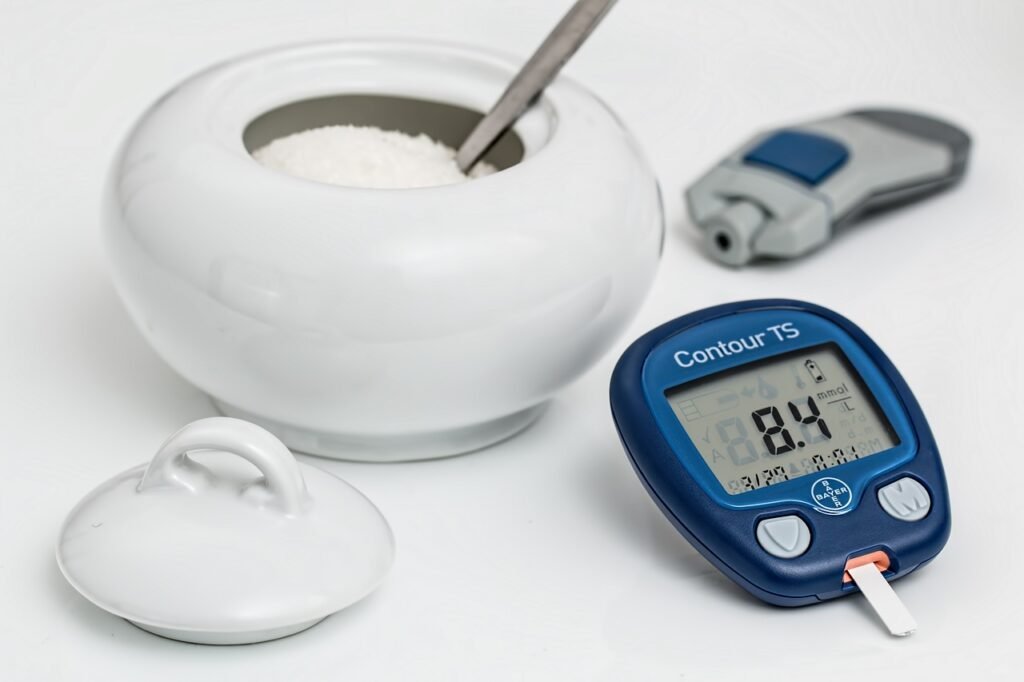
Significance of Blood Sugar Monitoring
Regular blood sugar monitoring is the cornerstone of diabetes management. By using a blood sugar monitor, individuals can track their levels, allowing for timely adjustments to medication, diet, and lifestyle. This proactive approach enables better control, reducing the risk of complications associated with poorly managed diabetes.
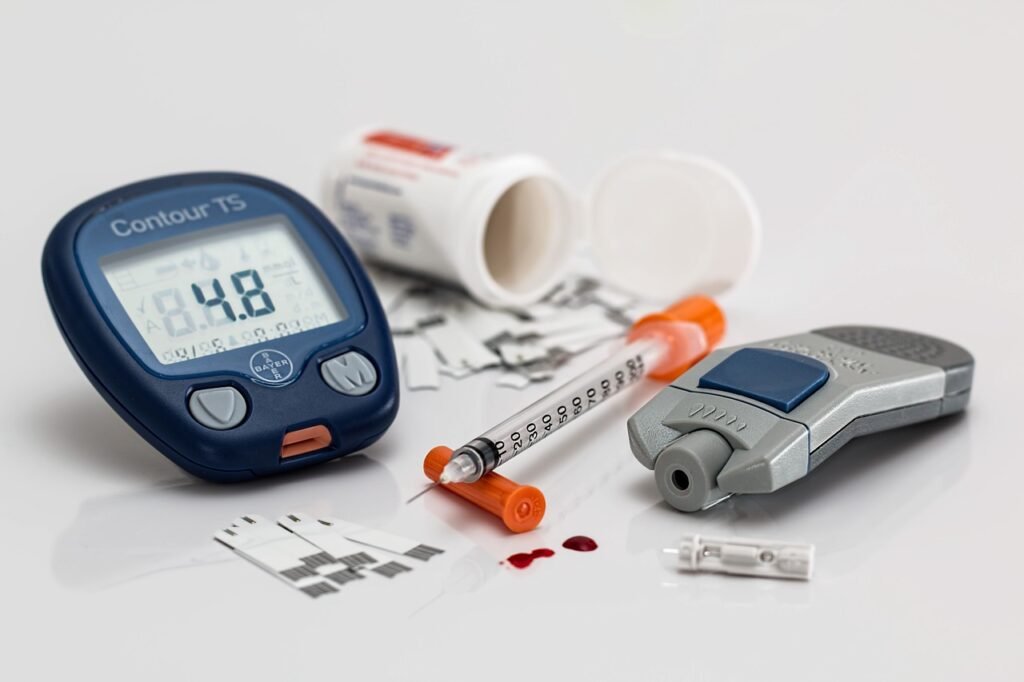
Effective Treatments for Diabetes
- Insulin Therapy: Essential for type 1 diabetes, insulin therapy may also be prescribed for some individuals with type 2 diabetes to regulate blood sugar levels effectively.
- Oral Medications: Type 2 diabetes management often involves oral medications, such as metformin, sulfonylureas, or thiazolidinediones, which help improve insulin sensitivity or reduce glucose production.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Incorporating regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption are fundamental in managing both types of diabetes.
Frequently Asked Questions Besides Symptoms And Treatement
Q1: What are the early signs of diabetes? A1: Early signs include increased thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, and fatigue. Timely recognition of these symptoms is crucial for early intervention.
Q2: Is there a cure for diabetes? A2: While there’s no cure, effective management through lifestyle changes, medications, and, in some cases, insulin therapy allows individuals to lead fulfilling lives.
Q3: How does continuous glucose monitoring work? A3: CGM involves a small sensor inserted under the skin, providing real-time data on blood sugar levels. This empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their diabetes management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, navigating the realm of diabetes requires a holistic understanding of Symptoms And Treatement. By incorporating continuous glucose monitoring, adopting a diabetic-friendly diet, and embracing proactive blood sugar monitoring, individuals can empower themselves to manage diabetes effectively. Armed with knowledge, one can embark on a journey towards a healthier, well-managed life with diabetes.
This comprehensive guide aims not only to educate but also to inspire proactive engagement in diabetes care, promoting overall well-being and a thriving life despite the challenges posed by this chronic condition.